
In a world that never slows down, precision and efficiency have become more than just buzzwords—they’re essential. That’s where laser marking machines step in, reshaping how we label and engrave materials with unmatched accuracy.
Laser marking machines are primarily used in industries such as electronics, jewelry, and pharmaceuticals for tasks like engraving, etching, and annealing on metals and non-metals. Their ability to create precise, permanent markings makes them indispensable in quality control and product identification.
While the basics of laser marking are interesting, delving into specific applications across different sectors reveals just how versatile and impactful these machines truly are. Let’s take a closer look!
Fiber lasers are ideal for marking metals.True
Fiber lasers excel in marking metals due to their high precision and efficiency.
How Do Fiber Lasers Benefit the Electronics Industry?
Fiber lasers are revolutionizing the electronics industry with their precision and versatility. But how exactly do they benefit manufacturers and consumers alike?
Fiber lasers benefit the electronics industry by offering high precision, speed, and efficiency in marking, cutting, and welding applications. They enable intricate designs on tiny components, enhance product durability, and reduce production costs.
Precision and Accuracy
In the electronics industry, precision is non-negotiable. Fiber lasers excel in delivering high-precision markings and cuts on electronic components. This accuracy is crucial for marking circuit boards1 and etching tiny electronic parts, where even the slightest error can lead to malfunctions. Fiber lasers achieve this through their ability to focus a high-intensity beam onto a small area, allowing for intricate and clean cuts without damaging the surrounding material.
Speed and Efficiency
Time is money in any industry, and fiber lasers offer unparalleled speed. They can process materials faster than traditional methods like mechanical cutting or CO2 lasers. This increased speed translates to shorter production cycles, enabling manufacturers to meet high-demand situations efficiently.
For example, fiber lasers are often used to mark serial numbers and barcodes on electronic components quickly and accurately. This rapid processing capability ensures that production lines continue moving without bottlenecks, directly contributing to a reduction in manufacturing costs.
Versatility Across Materials
Fiber lasers are not only precise but also versatile. They work exceptionally well with metals, which are commonly used in electronic devices. They are also effective on some non-metal materials like polymers used in electronics packaging. This adaptability makes them an invaluable tool for diverse electronic manufacturing processes.
Consider the marking of smartphone components: fiber lasers can etch logos on metal backs, cut openings for ports on cases, or mark identification numbers on circuit boards, showcasing their versatility in handling different tasks across various materials.
Enhanced Durability and Quality
Markings made by fiber lasers are resistant to wear and tear, ensuring that important information like serial numbers and QR codes remain legible throughout the product’s lifespan. This longevity is vital for product identification and quality assurance in consumer electronics.
Moreover, the non-contact nature of laser marking means there is minimal risk of mechanical damage during processing, preserving the integrity of sensitive electronic components.
Environmental Benefits
Fiber lasers also contribute to greener manufacturing processes. They have a high electrical efficiency and do not require consumables like inks or solvents. This leads to reduced waste and lower energy consumption compared to other laser technologies or traditional marking methods.
By adopting fiber lasers, manufacturers can align with sustainable practices while simultaneously improving productivity.
Understanding these advantages helps industry professionals appreciate why fiber lasers have become essential tools in modern electronics manufacturing. For more detailed insights into how fiber lasers impact electronic design2, further exploration into their specific applications is recommended.
Fiber lasers enhance product durability in electronics.True
Fiber lasers create wear-resistant markings, ensuring longevity.
Fiber lasers require consumables like inks or solvents.False
Fiber lasers are consumable-free, reducing waste and costs.
What Makes CO2 Lasers Ideal for Non-Metal Materials?
CO2 lasers are renowned for their versatility in working with a wide array of non-metal materials. But what makes them so special?
CO2 lasers are ideal for non-metal materials due to their wavelength, which is highly absorbed by organic materials, allowing for precise and efficient cutting or engraving without damaging the material.

Understanding CO2 Laser Technology
CO2 lasers operate at a wavelength of 10.6 micrometers, which is particularly well-absorbed by organic materials like wood, leather, and plastics. This absorption efficiency allows CO2 lasers to cut or engrave non-metal materials with high precision and minimal thermal damage. The wavelength’s suitability3 for non-metals is a key reason why industries prefer CO2 lasers for applications such as signage, decorative arts, and packaging.
Applications of CO2 Lasers
-
Signage and Advertising: CO2 lasers are extensively used to create intricate designs on acrylic and plastic materials. The ability to produce clean, precise cuts and engravings makes them indispensable in the advertising industry.
-
Textile Industry: CO2 lasers excel in cutting fabrics with intricate patterns. The non-contact process ensures that delicate materials like silk and lace maintain their integrity without fraying.
-
Crafts and Artworks: Artists and craftsmen use CO2 lasers to etch detailed patterns on wood, glass, and other non-metal surfaces, creating unique pieces of art that cannot be replicated by hand.
Comparing CO2 Lasers with Other Laser Types
| Laser Type | Suitable Materials | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| CO2 Laser | Non-metals like wood, glass | High precision, versatile applications |
| Fiber Laser | Metals and some plastics | High speed, durable markings |
| UV Laser | Delicate materials | Ultra-fine marking capabilities |
The comparison4 table above highlights why CO2 lasers are preferred for non-metal applications compared to other laser types. Their ability to work on a broad range of organic materials without causing damage makes them an excellent choice.
Advantages in E-Commerce and Personalization
In the world of e-commerce, the ability to offer personalized products can be a significant competitive advantage. CO2 lasers enable businesses to easily add custom engravings on items like phone cases and mugs, providing unique offerings to customers. This adaptability makes CO2 lasers a valuable tool for small businesses looking to diversify their product range and attract more customers.
For further insights into CO2 laser applications, check out our detailed guide5 on how these machines can transform your creative processes.
CO2 lasers operate at 10.6 micrometers.True
CO2 lasers have a wavelength of 10.6 micrometers, ideal for non-metals.
Fiber lasers are better for non-metal materials.False
Fiber lasers excel with metals; CO2 lasers are better for non-metals.
Why Choose UV Lasers for Pharmaceutical Packaging?
UV lasers are transforming pharmaceutical packaging with their precision and versatility, offering unparalleled benefits.
UV lasers are ideal for pharmaceutical packaging due to their high precision, ability to mark delicate materials, and compliance with industry regulations. These lasers provide clear, permanent markings essential for traceability and anti-counterfeiting measures.

Precision and Clarity
UV lasers offer unmatched precision, making them perfect for intricate designs and small font sizes required in pharmaceutical packaging. This is crucial for ensuring readability and compliance with regulatory standards. The laser’s short wavelength allows it to create fine marks without damaging the surrounding material, maintaining the integrity of the packaging.
Versatility in Materials
Pharmaceutical packaging often involves delicate materials such as plastics, films, and labels. UV lasers6 can mark a wide range of substrates without causing thermal damage. This versatility ensures that regardless of the material composition, the laser can produce clear and durable marks.
| Material Type | UV Laser Suitability | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Plastics | High | Blister packs |
| Films | High | Safety seals |
| Labels | High | Barcode labels |
Compliance with Regulations
The pharmaceutical industry is heavily regulated, requiring precise and permanent markings for traceability and anti-counterfeiting. UV lasers meet these requirements by producing marks that are resistant to wear and tear. This capability helps manufacturers adhere to stringent guidelines while ensuring product safety and authenticity.
Efficiency in Production
In high-speed production environments, UV lasers provide rapid marking without compromising quality. Their non-contact nature means less wear on equipment and minimal maintenance. This efficiency not only speeds up production lines but also reduces operational costs, making UV lasers a cost-effective solution for large-scale pharmaceutical manufacturing.
Environmental Considerations
Unlike some traditional marking methods, UV lasers do not produce harmful emissions or waste. This makes them an environmentally friendly option for companies aiming to reduce their carbon footprint. By using a UV laser, companies contribute to a cleaner production process while maintaining high-quality packaging standards.
UV lasers cause thermal damage to packaging.False
UV lasers mark without thermal damage, preserving material integrity.
UV laser markings are resistant to wear and tear.True
The markings are permanent and comply with industry regulations.
What Factors Should Guide Your Laser Marking Machine Selection?
Selecting the perfect laser marking machine requires careful consideration of material needs, precision, and production requirements.
When selecting a laser marking machine, consider the materials you will work with, precision needs, and production requirements. Fiber lasers suit metals, CO2 lasers are ideal for non-metals, and UV lasers offer ultra-fine precision. Balancing these factors ensures optimal performance and efficiency.
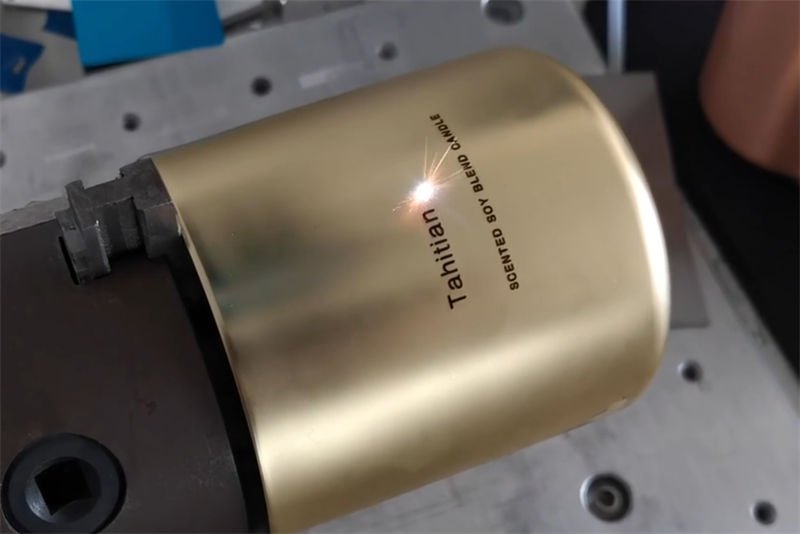

Understanding Your Material Needs
The first step in choosing a laser marking machine is identifying the materials you plan to work with.
- Fiber Laser Markers are optimal for metals such as stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium. They also work on some non-metals like glass and polymers. Industries like electronics and jewelry benefit greatly from their versatility.
- CO2 Laser Markers are designed for non-metal materials. They excel in processing wood, plastics, and fabrics, making them suitable for personalized engraving projects such as phone cases and signage.
- UV Laser Markers provide precise markings on a wide range of materials, perfect for intricate applications like micro-perforating pharmaceutical packaging.
Precision Requirements
Different applications demand varying levels of precision. For tasks requiring ultra-fine detail, such as complex pattern cutting or high-speed division of delicate materials, UV laser markers are unmatched.
| Laser Type | Precision Level | Suitable Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber | High | Electronics, jewelry, aerospace |
| CO2 | Moderate | Woodworking, signage, arts & crafts |
| UV | Ultra-High | Pharmaceuticals, microelectronics |
Evaluating Production Needs
Consider the scale of production and speed requirements. The power of the laser affects both marking depth and speed.
- A standard 20-watt fiber laser is often sufficient for most industrial applications but higher wattage might be needed for deeper engraving.
- CO2 lasers are typically used in medium-scale operations where speed is less critical but versatility is key.
- UV lasers cater to industries with stringent precision demands where speed can be secondary to accuracy.
Understanding these factors will guide your decision-making process and ensure you select a machine that meets your specific needs effectively. For more tailored advice on selecting the right laser for different industrial applications, consider consulting detailed laser selection guides7.
Fiber lasers are best for marking metals.True
Fiber lasers excel at marking metals like steel and aluminum.
CO2 lasers are unsuitable for non-metals.False
CO2 lasers are ideal for non-metals like wood and plastics.
Conclusion
In summary, laser marking machines are indispensable tools across various industries, enhancing branding and traceability. Investing in this technology can streamline operations and help meet rigorous industry standards.
-
Explore detailed benefits of fiber lasers in circuit board precision.: A laser will not warp and skew FR-4 material so this is a very nice way to have PCB made to size. It will burn edges though, but light touch … ↩
-
Understand how fiber lasers influence intricate electronic designs.: Fiber lasers are often used in laser welding, cutting, etching, and cleaning in different industries. Learn more about them here. ↩
-
Learn how specific wavelengths enhance laser precision on non-metals.: CO2 lasers have long wavelengths, around 9.3 – 10.6 µm … This is the absorption spectrum for polypropylene, with peaks indicating wavelengths with higher. ↩
-
Understand the key differences between CO2 and fiber lasers.: CO2 lasers consume considerably more power than fiber lasers for the same energy output, so their operational power costs are much higher. The … ↩
-
Discover creative uses of CO2 lasers in artistic projects.: CO2 lasers are valuable tools in the woodworking arsenal for precise cutting, engraving, and customization of wood materials. ↩
-
Discover detailed benefits of UV laser technology for packaging needs.: Discover the high-resolution, safe, and permanent solution for product laser marking in the food and pharmaceutical industries with KEYENCE’s laser marking. ↩
-
Discover in-depth advice on selecting suitable laser machines.: When choosing the appropriate laser marking machine, the following need to be taken into consideration: – Material properties: Each material … ↩



