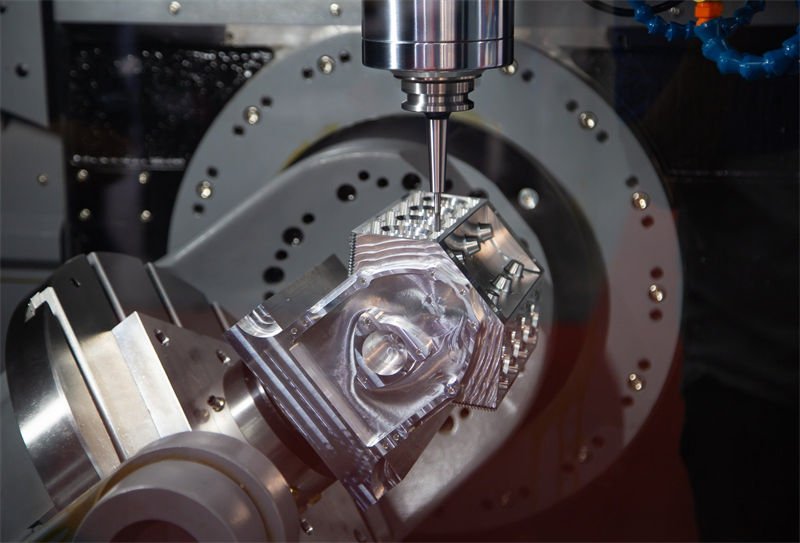
Imagine a world where every component of a machine is crafted with pinpoint accuracy—this is the reality created by CNC milling machines!
CNC milling machines are automated cutting devices that use computer controls to precisely machine materials into desired shapes. They function by following programmed instructions, enabling the creation of complex parts with high accuracy across various industries.
But there’s so much more than just the basics! Let’s delve into the fascinating details of how these machines operate, the intricacies of their programming, and how they adapt to diverse applications.
CNC milling machines are only used in aerospace.False
CNC milling machines are used in various industries, not just aerospace.
What Makes CNC Milling Machines So Precise?
CNC milling machines are synonymous with precision, essential for crafting intricate components across industries.
The precision of CNC milling machines is primarily due to their computerized control system, which ensures exact tool paths, reduces human error, and allows for the machining of complex shapes with micron-level accuracy. This precision is vital in industries like aerospace, automotive, and mold manufacturing.
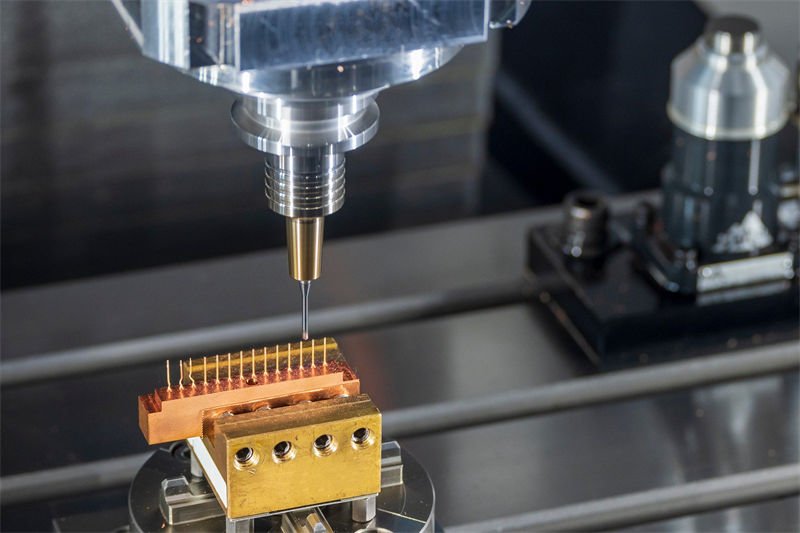
The Role of Computerized Control Systems
At the heart of CNC milling’s precision is its computerized control system1. This system controls the movement of the machine’s tools with high accuracy, minimizing human error. This precise control allows for complex, multi-axis movements necessary for creating detailed parts.
For example, in aerospace component manufacturing, the ability to control tool paths to the micron level ensures that each part fits perfectly within its assembly. This capability is achieved through advanced programming that dictates every movement of the tool.
Precision in Different Industries
Aerospace
In aerospace, the demand for precision is at its peak. Components like turbine blades require micron-level precision2 to maintain performance and safety standards. CNC milling machines meet these demands by enabling precise control over complex curved surfaces and tight tolerances.
Automotive
While not as stringent as aerospace, the automotive industry still requires high precision. Engine blocks and other critical components need to be machined within specific tolerance ranges (typically around ±0.05mm) to ensure performance and reliability.
Mold Manufacturing
In mold manufacturing, CNC milling machines are used to create complex cavities and cores that dictate the final product’s shape. Precision is crucial here to ensure that the molds produce consistent and defect-free parts.
Programming and Operation Expertise
The precision of CNC milling is also dependent on the expertise in programming and operation. Complex programming using software like Mastercam or UG NX ensures that tool paths are optimized for both precision and efficiency. Operators play a critical role in setting cutting parameters and handling tools to avoid errors during machining.
Material Machining Capabilities
CNC milling machines can handle a variety of materials, each requiring specific cutting parameters to maintain precision. For softer materials like aluminum alloys, higher cutting speeds can improve efficiency without sacrificing accuracy. In contrast, harder materials like die steel require careful selection of cutting tools and parameters to avoid tool damage while maintaining precision.
| Material | Cutting Tool Selection | Cutting Speed Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Alloys | High-speed steel or carbide | High |
| Die Steel | Carbide | Low to moderate |
| Plastics | High-speed steel | Moderate |
Through these elements, CNC milling machines consistently deliver high-precision results across various industries, meeting diverse needs from aviation to consumer goods manufacturing.
CNC milling machines reduce human error significantly.True
Computerized control systems ensure precise tool paths, reducing errors.
Micron-level precision is unnecessary in mold manufacturing.False
Precision is crucial for defect-free parts in mold manufacturing.
How Do Different Industries Utilize CNC Milling Machines?
CNC milling machines are essential across numerous industries, transforming how products are manufactured with precision and speed.
Industries use CNC milling machines to produce precise components, molds, and intricate parts from various materials. Their adaptability makes them vital in sectors like aerospace, automotive, and consumer goods manufacturing.
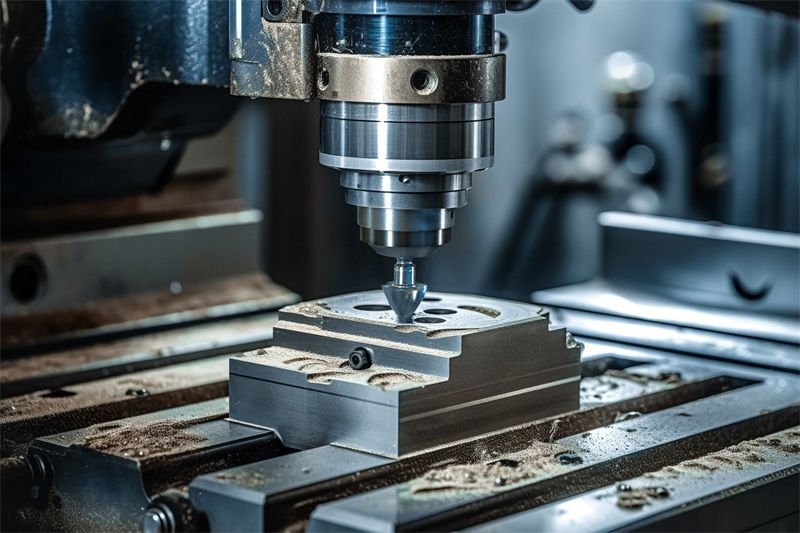

Aerospace Industry: Achieving Unmatched Precision
In the aerospace sector, precision is critical, with CNC milling machines often being the backbone of manufacturing. These machines handle the meticulous creation of components such as turbine blades and structural elements. The ability to achieve tolerances within microns ensures the reliability and performance of aircraft parts.
For example, when milling aircraft engine blades, the precision of each blade’s curvature is essential for optimal engine efficiency. CNC milling enables precise contouring and consistency, significantly reducing errors associated with manual machining.
Automotive Industry: Speed and Efficiency
CNC milling machines in the automotive industry focus on efficiency without compromising quality. They are used to produce engine blocks, transmission housings, and other critical components. The machines’ capability to work within a flatness precision of ±0.05mm allows manufacturers to maintain high standards while meeting production deadlines.
Manufacturers often utilize CNC machines to quickly switch between different part designs, adapting to model changes and new vehicle technology trends efficiently.
Mold Manufacturing: Complexity and Customization
Mold manufacturing is another area where CNC milling shines. It plays a pivotal role in creating complex injection and die-casting molds used for products ranging from toys to automotive parts.
Molds require detailed cavity and core shapes, achievable through the precision programming of CNC milling machines. This capability ensures that each mold meets exact specifications for high-quality product outputs.
Consumer Goods: Artistic and Functional Designs
In consumer goods, CNC milling is employed for both functional components and decorative items. From kitchen appliances to electronic gadgets, these machines carve out intricate designs that appeal to consumers while maintaining structural integrity.
The ability to work with various materials, including metals and plastics, makes CNC milling an ideal choice for producing diverse product lines.
Adapting to Material Challenges
CNC milling machines can process a variety of materials, from soft plastics to hard metals. For instance, in machining aluminum alloys, higher speeds enhance productivity due to the material’s lower hardness. Conversely, machining high-hardness die steel requires careful selection of cutting tools and parameters to maintain tool life and part quality.
These capabilities highlight the versatility of CNC milling across industries, enabling precise adaptation to each sector’s unique demands and materials.

As industries continue to evolve, exploring advanced technologies in CNC milling could further optimize production processes. Discover more about innovations that are shaping the future of manufacturing with CNC milling solutions.
CNC milling in aerospace achieves tolerances within microns.True
CNC milling ensures precise tolerances crucial for reliable aircraft components.
Automotive CNC milling maintains flatness precision of ±0.5mm.False
CNC milling in automotive industry maintains a precision of ±0.05mm.
What Are the Programming Challenges in CNC Milling?
Programming for CNC milling demands precision, adaptability, and deep process understanding to overcome inherent challenges.
Programming challenges in CNC milling arise from the need for precision, complex geometries, and material-specific considerations. Overcoming these challenges requires skilled operators proficient in both manual and automatic programming methods, ensuring efficient tool path planning and accurate execution.
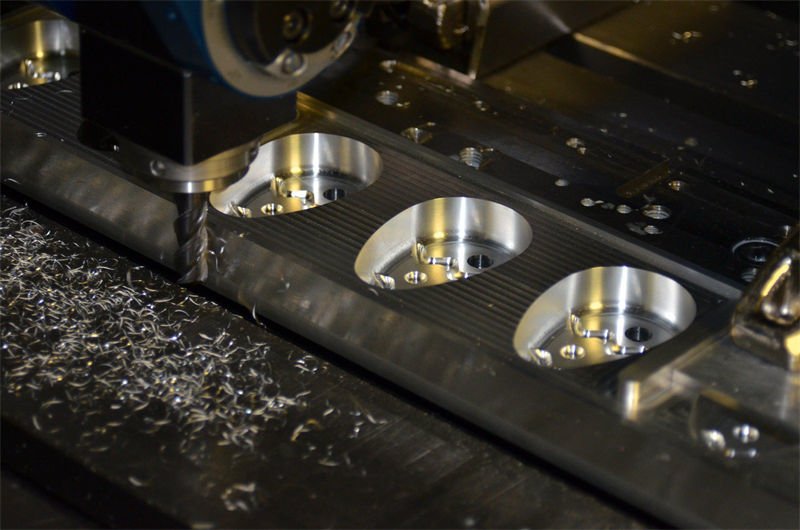

Complexity of Programming
One of the primary challenges in CNC milling programming is managing complex geometries. Simple parts might be easily programmed using manual techniques3, but intricate shapes require advanced software like Mastercam or UG NX. These tools automatically generate tool paths from 3D models, necessitating a thorough understanding of the software for effective use.
For instance, while programming a turbine blade, precise control over entry and exit points of the tool is essential to prevent tool marks. Hence, programmers must account for the tool path’s intricacies, considering part shape, material, and machine capabilities.
Flexibility in Programming
Operators must be flexible in choosing between manual and automated programming. Manual programming is ideal for straightforward tasks like plane milling, where G-code can be directly input. However, for complex surfaces, automatic programming is not just preferred but necessary to ensure optimal path planning and execution.
Moreover, programmers need in-depth knowledge4 of machining processes to set cutting parameters like speed, feed rate, and depth appropriately. This adaptability is vital for dealing with varying material properties and part specifications.
Skill Requirements for Operators
The skill level of operators significantly impacts programming success. They need to understand mechanical machining basics, such as cutting tool selection and fixture setup. For example, when machining thin-walled parts, choosing the right fixture is crucial to avoid deformation.
Furthermore, proficiency in operating the CNC machine panel is necessary. Operators should know how to input, edit, and run programs efficiently. Additionally, they must handle faults such as tool breakage or overload alarms swiftly to minimize downtime.
Case Study: Machining Aerospace Components
In aerospace manufacturing, precision is paramount. CNC milling machines handle this by following complex programming that accounts for tight tolerances and material specifics. For instance, the precision required for an aircraft engine blade can reach micron levels, demanding meticulous programming to achieve desired results.
In conclusion, while CNC milling offers unparalleled precision and efficiency, it poses substantial programming challenges. Navigating these demands a blend of technical skill, process knowledge, and adaptive programming strategies.
Advanced software is required for complex geometries.True
Complex shapes necessitate tools like Mastercam for tool path generation.
Manual programming is preferred for intricate CNC milling tasks.False
Automatic programming is necessary for complex surfaces, not manual.
How Does the Market Demand Influence CNC Milling Machine Development?
Market demand plays a pivotal role in shaping the advancements of CNC milling machines.
The evolution of CNC milling machines is heavily influenced by market demand, which drives manufacturers to innovate and adapt to industry-specific needs. Changes in economic conditions, technological advancements, and emerging industries all contribute to this dynamic development process.

Understanding Market Volatility
The demand for CNC milling machines5 is significantly impacted by fluctuations in the macroeconomic environment. During economic booms, industries like automotive and aerospace experience growth spurts, leading to increased purchases of CNC equipment. For instance, during the rise of electric vehicles, the need for precision components heightened, urging manufacturers to develop machines capable of delivering tight tolerances.
Conversely, economic downturns often result in reduced investments in new machinery. The 2008 global financial crisis serves as a prime example, where a decline in automotive sales led to a drop in CNC milling machine acquisitions. This cyclical nature forces manufacturers to remain agile, continuously assessing market conditions to align their production strategies.
Influence of Emerging Technologies
Technological advancements such as 3D printing have both challenged and spurred innovation within the CNC milling sector. While initially perceived as a threat, 3D printing has expanded the horizon for CNC applications by requiring post-processing solutions for printed parts. This synergy has catalyzed developments in hybrid machines that incorporate both additive and subtractive manufacturing capabilities.
For example, manufacturers are now focusing on enhancing surface finishing and precision post-treatment for 3D printed metal components6, ensuring that CNC milling remains a vital part of the production process in modern manufacturing settings.
Competitive Landscape and Innovation
The competition within the CNC milling industry is fierce, with global brands vying for market dominance. High-end manufacturers like DMG MORI and Mazak continue to invest in cutting-edge technologies such as five-axis machining and high-speed cutting to differentiate themselves. Their focus on reliability and advanced capabilities attracts high-value clients from industries requiring precision and efficiency.
Meanwhile, cost-effective solutions from emerging markets are gaining traction, especially among small to medium-sized enterprises. Chinese brands like Shenyang Machine Tool leverage cost advantages and technological improvements to offer competitive pricing without compromising on essential features. This duality in market demand propels innovation across different pricing segments, ensuring that all customer needs are met effectively.
The Role of Customer Expectations
Customers today demand more than just basic machining capabilities; they seek comprehensive solutions that enhance productivity and reduce operational costs. Factors such as energy efficiency, ease of maintenance, and integration with existing systems are increasingly becoming deciding factors.
Manufacturers respond by incorporating smart technologies into their CNC machines. These advancements include real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance capabilities, and enhanced user interfaces, all designed to meet evolving consumer expectations while maintaining competitiveness in the marketplace.
Market demand drives CNC milling innovation.True
Manufacturers innovate based on industry-specific needs and economic trends.
3D printing eliminates the need for CNC milling.False
3D printing requires CNC for post-processing, enhancing precision.
Conclusion
CNC milling machines are indispensable in modern manufacturing, offering unparalleled precision and versatility. Understanding their operation and applications can greatly benefit those in engineering and production fields.
-
Explore how computer systems ensure precise tool movements.: CNC precision machining uses computer-controlled tools to create high-accuracy parts, regardless of complexity. Explore the process and … ↩
-
Understand the critical need for precision in aerospace components.: These small yet powerful devices have the potential to save lives, revolutionize industries, and deepen our understanding of the world. While … ↩
-
Learn how to manually program CNC machines for simpler operations.: This practical and very useful resource covers several programming subjects, including how to program cams and tapered end mills, that are virtually impossible … ↩
-
Explore the essential machining process knowledge for effective CNC operation.: 1. Paying Close Attention to Detail · 2. IT and Math Abilities · 3. Practical Abilities · 4. Problem-Solving · 5. Desire to Gain Expertise. ↩
-
Learn how market trends shape CNC machine innovations.: The global CNC Machine Market in terms of revenue was estimated to be worth $67.5 billion in 2023 and is poised to reach $80.4 billion by 2028, … ↩
-
Discover how CNC aids in finishing 3D printed components.: This guide covers the first step to part finishing, support removal, and the three categories of post-processing: Subtractive, Additive, and Material Changing. ↩



