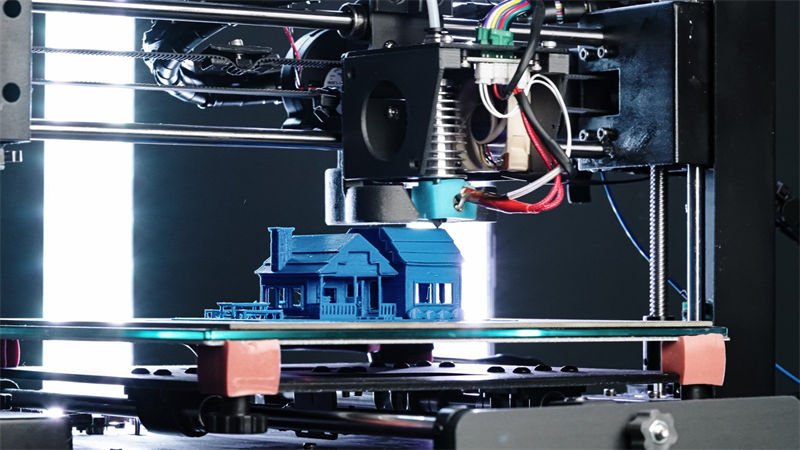
Have you ever wondered how to take your 3D printing projects to the next level? Carbon fiber filament might just be the key!
Yes, carbon fiber filaments are compatible with many 3D plastic printers. However, there are special requirements. For a successful print, a hardened steel nozzle is often necessary. Carbon fiber filaments are more abrasive than standard plastics, and an ordinary nozzle can get damaged quickly. Additionally, higher temperature settings are usually needed. The higher temperature helps in better melting and extrusion of the carbon fiber filament, allowing it to flow smoothly through the nozzle and adhere well to the print bed and previous layers, thus ensuring a high – quality 3D – printed object.
Let’s dive deeper into what you need to know about using carbon fiber in your 3D printing adventures!
Carbon fiber filaments need a hardened steel nozzle.True
The abrasive nature of carbon fiber wears down standard nozzles quickly.
What are the Essential Printer Modifications for Carbon Fiber Filaments?
Using carbon fiber filaments in 3D printing opens up new possibilities for stronger and more durable parts.
For using carbon fiber filaments, several essential printer modifications are necessary. Firstly, a hardened steel nozzle is a must. As carbon fiber is more abrasive than regular filaments, a standard nozzle would wear out quickly, but a hardened steel one can withstand this abrasion. Secondly, the printer should have the ability to reach high temperatures. Higher temperatures ensure the proper melting and flow of carbon fiber filaments. Lastly, combining a direct – drive extruder is beneficial. It provides better control over the filament feeding, which is crucial for achieving optimal printing results with carbon fiber filaments.

Understanding Printer Compatibility
Carbon fiber filaments possess unique properties that pose challenges in terms of printer compatibility. Unlike many common filaments, they are highly abrasive. When used with standard 3D printers not designed for such abrasiveness, the regular components can rapidly deteriorate. For instance, the nozzle, which is a crucial part in the extrusion process, is particularly vulnerable. Standard brass nozzles, commonly found in typical 3D printers, are not suitable for carbon fiber filaments as they would experience significant wear and tear in a short period. To address this issue, a hardened steel nozzle1 is highly recommended. The hardened steel has a much higher resistance to abrasion, enabling it to handle the carbon fiber filaments without getting damaged easily. This modification is essential to ensure the smooth and efficient operation of the 3D printer when using carbon fiber filaments and to prolong the lifespan of the nozzle and other related components.
Temperature Requirements
Printing with carbon fiber filaments necessitates higher temperatures compared to standard filaments. Ensure that your printer’s hot end can reach temperatures of at least 230°C. Some advanced models can handle even higher temperatures, which is beneficial for printing with certain carbon fiber composites like nylon or polycarbonate.
Choosing the Right Extruder
A direct drive extruder2 is preferable when working with carbon fiber filaments. These materials are often more brittle than standard filaments, and a direct drive system provides better control and reduces the risk of filament breakage.
Ensuring Proper Adhesion: Print Bed Considerations
Carbon fiber filaments require a heated print bed to ensure proper adhesion of the first layer. This is crucial for achieving a smooth print and preventing warping. Adjusting the bed temperature according to the base material of the filament (such as PLA, PETG, or ABS) can also enhance print quality.
Optimizing Print Speed and Filament Path
Reducing print speed when using carbon fiber filaments can lead to more consistent results and improved print quality. Additionally, having a well-guided filament path is essential to prevent breakage due to the brittle nature of these filaments. Ensure your printer’s filament path is optimized for smooth feeding.
Base Material Considerations
Carbon fiber is often combined with base materials like PLA, PETG, nylon, or ABS. Familiarize yourself with the printing settings for these materials as they form the foundation of your carbon fiber filament. For example, if you’re using a nylon-based filament, ensure your settings align with those typically used for nylon printing.
Implementing these modifications can significantly enhance your experience with carbon fiber filaments and unlock their full potential in your 3D printing projects.
Hardened steel nozzles are essential for carbon fiber filaments.True
They resist wear from the abrasive nature of carbon fiber.
A heated print bed is unnecessary for carbon fiber filaments.False
A heated bed ensures proper adhesion and prevents warping.
How Do Temperature Settings Affect Carbon Fiber Printing?
Temperature is a crucial factor in carbon fiber 3D printing, impacting adhesion, strength, and surface finish.
Temperature settings in carbon fiber 3D printing are vital as they influence layer adhesion, material flow, and the overall structural integrity of the print. Typically, carbon fiber filaments require higher temperatures compared to standard filaments, ensuring optimal bonding and strength.

Importance of Temperature in Carbon Fiber Printing
Temperature plays a pivotal role in the 3D printing3 process, especially when working with carbon fiber filaments. These filaments often require elevated temperature settings due to their composite nature. For instance, while standard PLA might print well at around 200°C, carbon fiber-infused PLA may need temperatures of at least 230°C or higher to ensure proper material flow and adhesion.
Effects on Layer Adhesion
The right temperature ensures that each layer of the print adheres properly to the previous one. If the extruder temperature is too low, the filament may not bond effectively, leading to weak and brittle prints. Conversely, excessively high temperatures can cause the filament to become too fluid, resulting in poor layer definition and possible stringing issues.
Material Flow and Nozzle Compatibility
Carbon fiber filaments are more abrasive than typical plastics, necessitating a hardened steel nozzle. The higher temperatures aid in maintaining a steady flow of material through this nozzle type. Without adequate heat, the filament might not melt thoroughly, leading to clogs and inconsistent extrusion.
Impact on Structural Integrity and Surface Finish
Higher temperatures generally improve the surface finish of carbon fiber prints. They enable smoother layers and reduce visible seams. Moreover, ensuring the correct temperature enhances the overall strength of the printed part, crucial for applications demanding durability.
Balancing Print Bed Temperature
A heated print bed is equally essential in carbon fiber printing. It prevents warping by ensuring that the initial layers adhere firmly to the bed. Depending on the base material mixed with carbon fiber (such as Nylon or ABS), the bed temperature may vary but generally remains higher than that required for regular filaments.
Adjusting these temperature settings accurately can be challenging but is vital for achieving high-quality prints with carbon fiber filaments.
Carbon fiber filaments print best at 200°C.False
Carbon fiber filaments typically require temperatures above 230°C.
Heated beds prevent warping in carbon fiber prints.True
Heated beds ensure initial layers adhere, reducing warping.
What Types of Carbon Fiber Filaments Are Available?
Are you curious about the different types of carbon fiber filaments for 3D printing? These filaments offer unique properties that can enhance your projects.
There are two primary types of carbon fiber filaments used in 3D printing: chopped carbon fiber and continuous carbon fiber, each with distinct advantages in strength and application.

Chopped Carbon Fiber Filaments
Chopped carbon fiber filaments are the most common type available for 3D printing. These filaments consist of small carbon fiber particles, usually less than one millimeter in length, dispersed within a base polymer such as PLA, ABS, Nylon, or PETG. The presence of chopped fibers in the filament enhances mechanical properties, such as strength and stiffness, while also improving wear resistance and heat stability.
One popular example is the eSUN carbon fiber ABS4, which combines ABS with carbon fiber to enhance rigidity and reduce weight. This makes it suitable for parts that require a high degree of strength without compromising on flexibility.
| Material Base | Carbon Fiber Content | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | ~20% | Enhanced rigidity, lightweight |
| Nylon | ~20% | High heat resistance |
| PLA | ~15%-20% | Improved dimensional stability |
Continuous Carbon Fiber Filaments
In contrast to their chopped counterparts, continuous carbon fiber filaments integrate long strands of carbon fiber into the material. These filaments provide superior strength and load distribution, making them ideal for applications that demand structural integrity.
A notable example is the composite material produced by UltiMaker, which utilizes continuous carbon fibers to significantly increase temperature resistance and part strength. Such enhancements make continuous carbon fiber filaments a perfect fit for the aerospace industry, where weight-to-strength ratio is critical.
While more expensive, these filaments are essential for high-performance components, offering a strength-to-weight ratio three times that of aluminum and a weight seven times lighter than steel.
Comparing the Two Types
When deciding between chopped and continuous carbon fiber filaments, consider the specific needs of your project:
- Chopped Carbon Fiber: Best for general-purpose applications where enhanced mechanical properties are desired at a reasonable cost.
- Continuous Carbon Fiber: Suited for critical applications requiring maximum strength and durability, albeit at a higher cost.
Both types expand the possibilities for 3D printing applications5 across various industries, providing innovative solutions for complex design challenges.
Chopped carbon fiber filaments are more common than continuous.True
Chopped carbon fiber filaments are widely available and used in 3D printing.
Continuous carbon fiber filaments are cheaper than chopped ones.False
Continuous carbon fiber filaments are more expensive due to higher strength.
What Are the Real-world Applications of Carbon Fiber 3D Printing?
Carbon fiber 3D printing is revolutionizing industries by offering lightweight, strong, and versatile solutions.
Carbon fiber 3D printing is extensively used in aerospace, automotive, sports equipment, and industrial tooling due to its lightweight and high-strength properties.
Aerospace Innovations
Carbon fiber 3D printing has made significant strides in the aerospace sector. The ability to produce components that are lightweight yet extremely strong is a game-changer. For instance, Boeing has leveraged this technology to manufacture large-scale parts for its 777X passenger planes. These components are not only lighter than traditional metal parts but also reduce the overall manufacturing costs and time.
Moreover, partnerships such as the one between miniFactory and the Royal Netherlands Aerospace Center highlight ongoing advancements. They are working on using carbon fiber 3D printing to develop parts that can withstand the extreme conditions of space travel, ensuring durability and reliability.
Automotive Advancements
The automotive industry is rapidly adopting carbon fiber 3D printing to enhance vehicle performance. Companies like AREVO and Superstrata have pioneered the creation of bike frames entirely from continuous carbon fiber composites. These frames boast enhanced strength without the added weight, resulting in increased efficiency and better handling.
In addition to bicycles, car manufacturers are exploring carbon fiber 3D printing for various components, ranging from engine parts to interior elements. This approach not only improves fuel efficiency due to reduced weight but also enhances safety by using materials with superior impact resistance.
Sports Equipment Revolution
Sports equipment manufacturers are utilizing carbon fiber 3D printing to design gear that is not only lightweight but also exceptionally durable. From tennis rackets to golf clubs, the use of continuous carbon fiber ensures that athletes can perform at their best without being weighed down by their equipment.
For example, some companies have started producing ski poles with carbon fiber 3D printing technology, providing skiers with more control and agility on the slopes.
Industrial Tooling and Prototyping
In industrial settings, carbon fiber 3D printing is invaluable for creating robust tooling and functional prototypes. The ability to quickly iterate designs and test them in real-world conditions saves both time and resources.
This technology enables manufacturers to produce customized tools that are specifically tailored for particular tasks, enhancing efficiency and reducing wear-and-tear on machinery.
| Application Field | Benefits of Carbon Fiber 3D Printing |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Lightweight components, cost reduction, rapid manufacturing |
| Automotive | Improved fuel efficiency, superior strength, enhanced safety |
| Sports Equipment | Lightweight gear, increased durability, enhanced athletic performance |
| Industrial Tooling | Customization, quick prototyping, reduced production costs |
In conclusion, while this is not an exhaustive list of applications, carbon fiber 3D printing continues to open new avenues across diverse industries. The versatility and strength of carbon fiber composites provide innovative solutions6 that drive progress and efficiency.
Boeing uses carbon fiber 3D printing for 777X parts.True
Boeing manufactures large-scale 777X plane parts using this technology.
Carbon fiber 3D printing reduces automotive safety.False
It enhances safety by using materials with superior impact resistance.
Conclusion
Using carbon fiber filament can elevate your 3D printing game, offering enhanced strength and reduced weight. Ensure your printer is ready to maximize these benefits.
-
Hardened steel nozzles resist wear from abrasive materials.: Hardened nozzle to withstand the abrasiveness of the CF. Hardened extruder to not wear down the extruder components with the abrasiveness of the … ↩
-
Direct drive extruders offer precise control and minimize breakage.: The benefits of direct drive is that the shorter filament path allows for much better control over filament retraction and nozzle pressure. ↩
-
Understand why temperature is crucial for successful 3D printing.: The right temperature ensures proper filament flow, adhesion, and the overall structural integrity of the printed object. Inadequate temperature … ↩
-
Explore eSUN’s combination of ABS with carbon fiber for enhanced performance.: eABS-CF has excellent impact resistance and chemical corrosion resistance, and it has good performance in some scenarios with high strength demand such as … ↩
-
Discover how continuous carbon fibers innovate design across industries.: Continuous Fibers enable Markforged composite printers to print metal-strength parts. They cannot be used alone — however, when printed with a Composite Base, … ↩
-
Explore various industries benefiting from carbon fiber 3D printing technology.: Carbon Fiber 3D printing can be used to create prototypes that not only prove the designer’s concept but also allow the designer to functionally test their part … ↩



