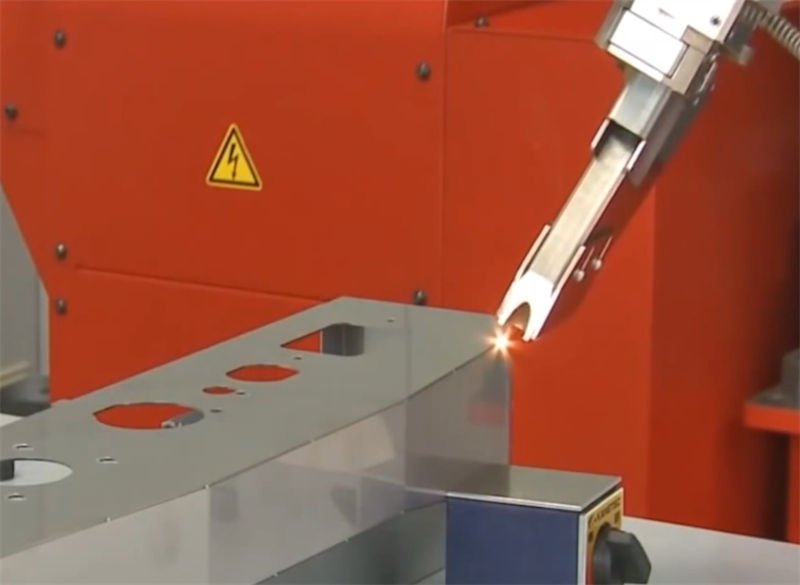

Are you considering laser welding for your next project but unsure if it’s the right choice?
The advantages of laser welding are high welding quality with beautiful welds, high strength and precision. The heat-affected zone is small, reducing workpiece deformation. It has fast welding speed, can weld a wide range of materials, has good flexibility, can achieve non-contact welding and is easy to automate, and has low requirements for the working environment. The disadvantages are high equipment cost, strict requirements for welded parts in terms of assembly accuracy and surface quality. When welding thicker workpieces, the welding depth is limited. There is a risk of welding defects such as pores and there are safety risks from laser radiation.
While this initial overview provides a glimpse into laser welding’s benefits and limitations, I invite you to delve deeper into each aspect to better prepare yourself for making a well-informed decision. Let’s explore these dimensions further.
Laser welding offers unmatched precision over traditional methods.True
Laser welding's high energy density allows for precise, focused welds.
How Does Laser Welding Compare to Traditional Methods?
Curious about how laser welding stacks up against traditional methods like arc or MIG welding?
Compared with traditional methods, laser welding is outstanding in terms of precision, speed, efficiency, minimum thermal deformation, weld aesthetics, internal quality, applicable material range and flexibility. Its weld is beautiful and has good internal quality and a wide range of applicable materials. However, laser welding equipment is expensive and has high operation requirements. Traditional welding technology has advantages in welding thicker materials and is cost-effective. However, its welding speed is slow, it is prone to defects, and the applicable materials are limited. Some operations rely on experience. Assessing specific needs can guide the choice between the two.
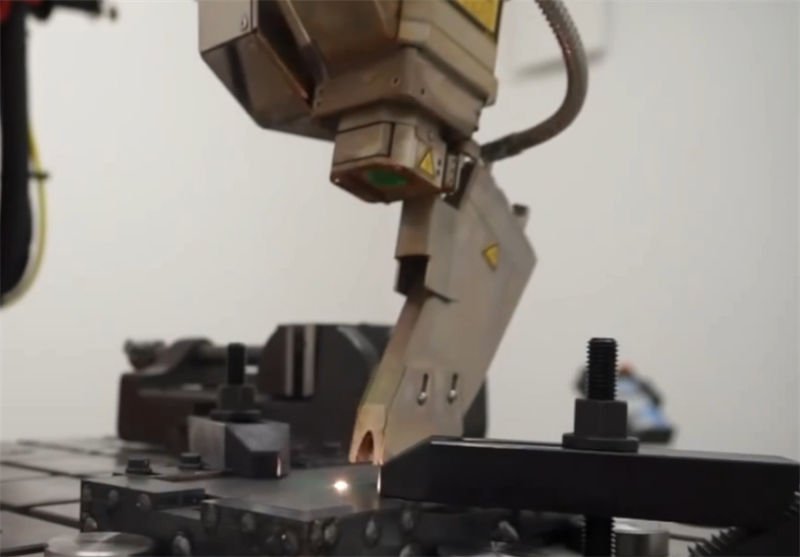

Precision and Heat Affected Zone (HAZ)
One of the primary distinctions between laser welding and traditional methods lies in precision. Laser welding offers unmatched accuracy due to its high energy density and ability to focus on a small area. This results in a significantly smaller heat affected zone (HAZ) compared to traditional welding techniques1. A smaller HAZ is crucial when working with materials sensitive to heat, as it minimizes thermal distortion and preserves the mechanical properties of the workpiece.
Traditional methods such as arc welding often result in larger HAZs, which can lead to increased deformation and may require additional processing to correct.
Speed and Automation
Laser welding also outpaces traditional methods in terms of speed, particularly in mass production settings where automation is feasible. The process can be easily integrated with robotic systems, allowing for high-speed, consistent welds with minimal human intervention. This automation capability enhances productivity and reduces labor costs.
In contrast, traditional welding methods like MIG or TIG require more manual operation, which can slow down production and increase costs over time.
Cost Implications
Despite its benefits, laser welding comes with a hefty price tag due to the cost of equipment and setup. Initial investment in laser systems is substantial compared to more established methods like stick or MIG welding. However, for industries requiring high precision and speed, such as automotive or aerospace, the long-term benefits can outweigh these initial costs. For businesses evaluating whether the cost of laser welding2 is justified, considerations include the scale of production and required precision.
Material Compatibility and Limitations
Laser welding is versatile across a wide range of materials, including metals and some plastics. It excels in joining dissimilar materials without the need for additional filler metals, which can be a challenge for traditional methods. However, its effectiveness diminishes with thicker materials; laser systems typically struggle beyond certain thicknesses due to limited penetration depth.
Traditional methods are generally more forgiving with thicker materials and complex joints, offering robustness where laser systems may not suffice.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice
Ultimately, choosing between laser and traditional welding depends on the specific requirements of your project. If precision, speed, and automation are critical, laser welding may be the superior choice despite higher costs. Conversely, for applications involving thicker materials or where budget constraints are tighter, traditional methods may prove more practical.
Consider assessing your production needs and material specifics before deciding on a welding method that best suits your objectives.
Laser welding has a smaller heat affected zone (HAZ).True
Laser welding's precision reduces the HAZ, minimizing thermal distortion.
Traditional welding is faster than laser welding in mass production.False
Laser welding is faster due to automation and high-speed capabilities.
What Are the Safety Concerns Associated with Laser Welding?
Laser welding, while efficient and precise, comes with unique safety challenges that need addressing.
Safety issues of laser welding include: first, laser radiation can cause corneal burns, retinal damage or skin burns in the eyes; second, smoke and harmful gases can damage the respiratory tract and lungs; third, electrical faults may cause electric shock; fourth, high-temperature spatter can burn the skin; fifth, there is an explosion risk when working in an environment with flammable and explosive substances .

Understanding Laser Radiation Hazards
One of the most significant risks in laser welding is the potential for eye injuries. The intensity of laser beams can cause severe damage to the retina, potentially leading to partial or complete blindness. To combat this, operators must wear appropriate laser safety goggles specifically designed to block harmful wavelengths. Additionally, workspaces should be equipped with protective barriers and warning signs to minimize accidental exposure.
Managing Skin Exposure Risks
Skin burns are another concern, as the laser’s concentrated energy can cause serious burns upon contact. Operators should wear protective clothing that covers the skin entirely to prevent accidental exposure. It’s also advisable to implement remote operation capabilities where feasible, reducing the need for operators to be in close proximity to the welding site.
Addressing Hazardous Fume Emissions
Laser welding can produce toxic fumes and gases, especially when working with materials like plastics or metals that contain coatings. Inhaling these fumes can have detrimental health effects. Thus, installing effective ventilation systems or local exhaust ventilation (LEV) is essential to capture and filter out harmful substances. Regular air quality assessments ensure that these systems function effectively.
The Role of Safety Protocols and Training
Comprehensive safety protocols are crucial for minimizing risks in laser welding environments. These protocols should include detailed procedures for equipment handling, maintenance, and emergency responses. Regular training sessions keep all personnel updated on the latest safety practices and technology advancements. By cultivating a strong safety culture, organizations can significantly reduce workplace accidents.
Implementing Safety Technology
Incorporating advanced safety technology can further enhance protection. For instance, integrating laser interlock systems3 prevents accidental activation of the laser beam when unauthorized access is detected or if the protective enclosures are breached. Additionally, real-time monitoring systems4 can detect hazardous fume levels, ensuring immediate action if thresholds are exceeded.
By understanding and addressing these safety concerns through proper equipment use, protective gear, and comprehensive training programs, organizations can harness the benefits of laser welding while maintaining a safe work environment.
Laser welding can cause eye injuries without goggles.True
Laser beams can damage the retina, requiring safety goggles.
Ventilation systems are unnecessary in laser welding.False
Ventilation is crucial to filter toxic fumes from materials.
How Do Material Types Affect Laser Welding Effectiveness?
Laser welding’s effectiveness hinges significantly on the type of material being welded.
The influence of material types on laser welding effects is mainly reflected in the following aspects. Firstly, the melting point of the material is very crucial. Materials with high melting points require more energy to be welded properly. For example, high-melting-point materials like tungsten are more difficult to weld than low-melting-point materials like aluminum. Secondly, there are differences in the absorption capacity of materials for lasers. Materials that absorb more lasers are welded more smoothly. Just like dark-colored materials may absorb lasers better than light-colored materials. Moreover, the thermal conductivity of materials also has an impact. If the material conducts heat too quickly, heat is easily lost, and welding will become more difficult. For example, copper has strong thermal conductivity, so welding copper requires special methods.
Reflectivity and Thermal Conductivity
The reflectivity and thermal conductivity of a material are critical in determining how effectively it can be laser welded. Materials like aluminum and copper have high reflectivity and thermal conductivity, which means they tend to reflect much of the laser energy instead of absorbing it. This can lead to inconsistent welds or require more energy to achieve desired results.
To counteract these challenges, techniques such as surface preparation to reduce reflectivity or using lasers with specific wavelengths that are better absorbed by these materials can be employed. Additionally, adjusting laser parameters like power density and focus can also help in achieving better weld quality.
Material Thickness
The thickness of the material plays a significant role in laser welding effectiveness. While laser welding is excellent for thin sheets due to its precision and minimal heat distortion, it struggles with thicker materials. This is because the laser’s energy may not penetrate deeply enough, leading to incomplete welds.
For instance, materials exceeding 19mm in thickness typically require alternative welding methods, as laser welding may not achieve sufficient depth and strength. However, advancements in laser technology continually push these boundaries.
Compatibility of Dissimilar Materials
Laser welding allows for the joining of dissimilar materials, which is a unique advantage over traditional methods. This capability is particularly beneficial in industries like automotive and aerospace, where different materials are combined for optimized performance.
However, the challenge lies in the differing melting points and thermal expansion coefficients of the materials. Successful welding of dissimilar metals often requires careful control of the laser parameters and may involve pre-welding or post-welding treatments to ensure joint integrity.
Special Material Considerations
Materials such as titanium alloys5 and plastics present unique challenges and advantages in laser welding. Titanium alloys, for example, require an inert gas environment to prevent oxidation during welding. Laser welding is particularly suited for plastics due to its ability to precisely control heat application, reducing risks of material degradation.
| Material | Challenges | Techniques for Improvement |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | High reflectivity | Surface preparation, wavelength adjustment |
| Copper | High thermal conductivity | Power density control |
| Titanium Alloys | Oxidation risk | Inert gas environment |
| Plastics | Heat sensitivity | Precise heat control |
Understanding how material types affect laser welding is crucial for achieving optimal results. By considering factors such as reflectivity, thermal conductivity, and thickness, and employing appropriate techniques, manufacturers can ensure high-quality welds across a range of materials.
Aluminum requires surface prep for effective laser welding.True
Aluminum's high reflectivity necessitates surface preparation to reduce energy loss.
Laser welding is best for materials over 19mm thick.False
Laser welding struggles with thick materials, often needing alternative methods.
Is the Cost of Laser Welding Justified by Its Benefits?
Laser welding is celebrated for its precision and efficiency, but does its cost truly outweigh the benefits?
Yes, the cost of laser welding is justified. In scenarios with high quality requirements, mass production and welding of special materials, the advantages of high quality, efficiency and flexibility of laser welding compensate for its high cost, and the two are commensurate.
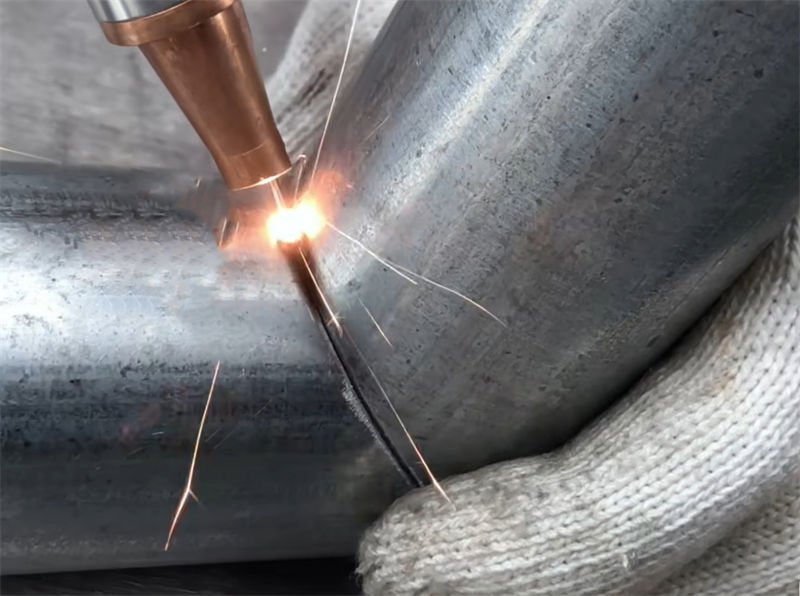

The Precision Advantage
One of the most compelling reasons to invest in laser welding is its unparalleled precision. The focused laser beam allows for tight control over the weld, reducing the risk of heat distortion. This is particularly beneficial when working with sensitive or thin materials that traditional methods might damage. Industries such as automotive manufacturing6 rely heavily on this precision to ensure quality and consistency in their products.
Speed and Efficiency
Laser welding can significantly enhance production speed. Its ability to perform at high speeds without compromising quality makes it a valuable asset in large-scale manufacturing. For example, in the aerospace sector7, where time and efficiency are crucial, laser welding’s ability to automate and accelerate processes can lead to substantial cost savings.
Versatility Across Materials
Laser welding’s versatility is another key benefit. It can effectively join a wide range of materials, from metals to plastics, and even dissimilar materials like steel and aluminum. This capability is crucial in industries where different materials need to be fused without compromising structural integrity or functionality.
High Initial Costs
Despite these advantages, the upfront cost of laser welding equipment is a significant barrier. The technology requires substantial investment in high-power lasers, cooling systems, and precise control systems. However, for industries with stringent quality requirements, such as medical devices8, this investment is often justified by the improved end-product quality and reduced defect rates.
Long-Term Savings
While the initial expenditure is high, laser welding can lead to long-term savings through reduced material waste and lower labor costs due to automation. Additionally, the minimal need for post-weld processing and reduced energy consumption compared to traditional methods can further offset the initial investment over time.
Considerations for Adoption
When deciding whether to adopt laser welding, companies should consider not just the cost but also the specific needs of their operations. In environments where precision, speed, and material versatility are paramount, the benefits of laser welding can far outweigh the costs.
| Feature | Traditional Welding | Laser Welding |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Distortion | High | Minimal |
| Material Versatility | Limited | Wide Range |
| Speed | Moderate | High |
| Initial Equipment Cost | Low | High |
| Automation Potential | Low | High |
Laser welding reduces material waste significantly.True
Laser welding's precision minimizes excess material use, cutting waste.
Initial costs of laser welding are lower than traditional methods.False
Laser welding equipment requires high initial investment compared to traditional methods.
Conclusion
In weighing the pros and cons of laser welding, consider your project’s specific needs. Precision and speed may justify the costs, while traditional methods could be more practical for thicker materials.
-
Explore why traditional welding might be more suitable in some scenarios.: Minimal thermal impact on the surrounding surfaces · Decreased post-weld processing costs · Lasers increase weld speed · Versatility. ↩
-
Understand the financial implications of choosing laser welding.: Traditional welding requires lower investment costs in comparison to laser welding. This makes the traditional welding method suitable for fabrication work … ↩
-
Learn how laser interlock systems enhance workplace safety.: Interlocks are safety devices for automatically switching off a laser power or interrupting a laser beam. ↩
-
Discover how real-time monitoring protects against fume hazards.: Some welding shops in the US are making use of the TSI® DustTrak™ Aerosol Monitor to measure airborne concentration levels of welding related smoke and fume in … ↩
-
Learn how to prevent oxidation when welding titanium alloys.: The most common method of joining titanium is the gas tungsten-arc (GTAW) process and, secondarily, the gas metal-arc (GMAW) process. ↩
-
Learn how automotive industries benefit from laser welding’s precision.: Laser welding certainly helps manufacturers in the automotive industry achieve higher quality, efficiency, and flexibility in their production … ↩
-
Discover why aerospace relies on laser welding for efficiency.: Aerospace Laser welding offers you high levels of accuracy. Therefore, making it a favourable technique for a consistently excellent standard of work. You can … ↩
-
Explore how medical device quality improves with laser welding.: Medical Device Laser Welding. Laser welding is the process of joining similar or dissimilar materials with exceptional strength and durability. ↩



