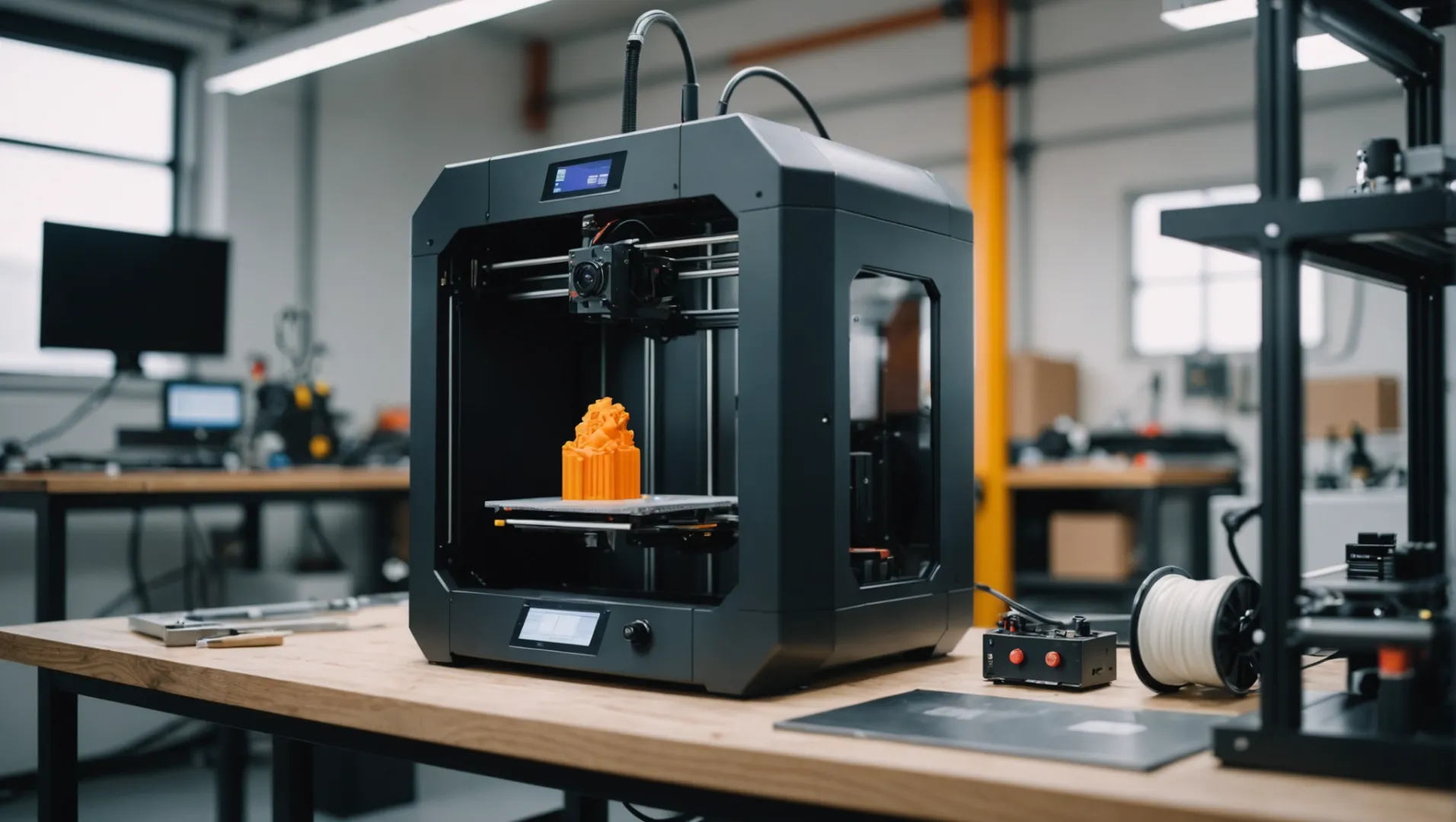

In the whirlwind of product development, I often find myself racing against time. That’s when I discovered 3D printing—a true game-changer in rapid prototyping.
3D printers play a crucial role in accelerating rapid prototyping. They permit rapid design iterations as changes can be easily made and new prototypes printed promptly. Cost reduction is significant as it eliminates the need for expensive molds and tooling. Complex designs that are difficult or impossible with traditional methods can be achieved, saving time and effort in design and manufacturing. The streamlined workflow shortens the product development cycle. Overall, 3D printers enhance the speed and flexibility of prototyping, thus promoting innovation and efficient product development.
But there’s so much more to this technology than just speed. Join me as we explore the profound impact of 3D printing on product development.
3D printing eliminates the need for traditional tooling.True
3D printing directly creates prototypes from digital models, bypassing tooling.
What Makes 3D Printing Faster Than Traditional Methods?
3D printing is transforming manufacturing by drastically reducing the time required to create prototypes compared to traditional methods.
3D printing offers faster production compared to traditional methods for several reasons. Firstly, it enables rapid design iterations. Design changes can be made digitally and printed immediately, without the need for retooling. Secondly, the elimination of tooling requirements saves significant time. Traditional manufacturing often requires the creation of molds or jigs which is time-consuming. Lastly, enhanced material efficiency means less waste and quicker build-up of the product. These aspects combined allow 3D printing to cut down production times and adapt to changes more swiftly.

Speed Through Rapid Iterations
One of the foremost reasons 3D printing is faster is its ability to rapidly iterate designs. In traditional methods, each design alteration might require new molds or tooling, which can be time-consuming and expensive. Conversely, with 3D printing, designers can swiftly modify digital CAD models to create updated prototypes in a matter of hours.
Consider the example of developing a new smartphone case. With 3D printing technology1, adjustments to the design for better ergonomics or button placement can be swiftly made and printed, allowing multiple iterations within a single day. This agility accelerates the design process considerably.
Elimination of Tooling Requirements
Traditional manufacturing often involves creating molds or tools, which not only adds time but also increases costs. 3D printing eliminates these steps entirely. By directly translating digital models into physical objects, it bypasses the need for any intermediary tooling. This direct approach ensures a smoother and quicker transition from concept to prototype.
For instance, manufacturing a complex part like a turbine blade conventionally requires detailed mold-making processes, whereas 3D printing methods2 can produce intricate parts directly from CAD files without any molds.
Enhanced Material Efficiency
3D printing is an additive process, meaning materials are added layer by layer only where needed. This contrasts with traditional subtractive manufacturing, which often involves cutting away excess material. The additive nature not only reduces waste but also speeds up the preparation and production stages.
To illustrate, when creating a lattice-structured component, traditional methods might struggle with material wastage and time-consuming milling processes. In contrast, 3D printers use only the necessary material, optimizing both time and resources.
Integrated Production Capabilities
Another factor contributing to the speed of 3D printing is its ability to print complex assemblies as a single unit. Where conventional methods might require multiple parts to be manufactured separately and then assembled, 3D printing can handle these tasks in one go.
Take the example of a robotic arm prototype that traditionally involves separate machining and assembly of joints. With integrated 3D printing3, these parts can be produced as a whole, saving considerable assembly time and reducing potential errors in assembly.
The combination of rapid iteration, elimination of tooling, efficient material use, and integrated production makes 3D printing a significantly faster alternative to traditional manufacturing methods.
3D printing requires molds for every design change.False
3D printing does not require molds, allowing quick design changes.
3D printing minimizes material waste compared to traditional methods.True
Additive manufacturing uses material only where needed, reducing waste.
How Does 3D Printing Reduce Prototyping Costs?
3D printing has revolutionized prototyping by significantly cutting costs across multiple stages of product development.
3D printing reduces prototyping costs in multiple ways. It eliminates the need for costly traditional tools such as molds and dies. With 3D printing, the digital design can be directly printed without the elaborate and expensive tooling process. It also minimizes material waste as it uses only the necessary amount of material for the prototype. Moreover, the simplified process requires less labor. Fewer steps and less manual intervention mean lower labor costs. Overall, these factors contribute to significant cost savings in prototyping.

Elimination of Expensive Tooling
One of the most significant cost-saving aspects of 3D printing technology4 is its ability to eliminate the need for expensive molds and tooling. In traditional manufacturing methods like injection molding, the creation of each prototype iteration necessitates a new mold, which can be both time-consuming and costly. However, with 3D printing, digital models are directly translated into physical prototypes, bypassing the need for molds entirely.
For instance, in industries such as automotive or aerospace, where prototypes often require intricate designs, the absence of tooling costs allows companies to produce multiple iterations without incurring additional expenses. This capability significantly reduces the financial barrier to innovation and experimentation.
Material Waste Reduction
3D printing employs an additive manufacturing process, using only the material necessary to create the prototype. This approach contrasts with traditional subtractive methods, where excess material is removed and discarded. The efficiency of material usage in 3D printing not only reduces costs associated with raw materials but also minimizes environmental impact by decreasing waste.
Consider a scenario where a company is prototyping a series of complex components with intricate geometries. Traditional methods would generate substantial waste as materials are carved away to achieve the desired shape. In contrast, 3D printing builds up the structure layer by layer, ensuring materials are only used where needed, thus saving both money and resources.
Decreased Labor Expenses
The automation inherent in 3D printing significantly lowers labor costs associated with prototyping. Traditional prototyping often requires skilled labor to operate machinery or assemble parts, leading to increased personnel expenses. With 3D printing, once the design is finalized in CAD software, the printer can autonomously produce the prototype, reducing the need for manual intervention.
Moreover, companies can keep prototyping processes in-house thanks to desktop 3D printers, eliminating outsourcing costs. By reducing reliance on external vendors for prototype production, businesses gain greater control over timelines and budgets while ensuring confidentiality and security of proprietary designs.
Versatile Material Choices
3D printing’s ability to utilize a diverse range of materials also contributes to cost savings. Prototyping often requires testing different materials to find the best fit for functionality and performance. With versatile 3D printers5, companies can experiment with various materials such as plastics, metals, or composites without switching between different machines or processes.
This flexibility means that companies don’t need to invest in specialized equipment for each material type, further reducing capital expenditure. Additionally, quick material swaps in 3D printers expedite the prototyping process and allow for rapid testing under various conditions.
3D printing eliminates the need for expensive molds.True
3D printing uses digital models, bypassing molds, saving time and cost.
Traditional prototyping produces less material waste than 3D printing.False
3D printing's additive process minimizes waste compared to subtractive methods.
Can 3D Printing Handle Complex Designs Effectively?
3D printing opens new frontiers in design freedom, allowing intricate geometries that traditional methods struggle to achieve.
Yes, 3D printing can handle complex designs effectively. The layer – by – layer construction method is its key advantage. It eliminates many of the limitations of traditional manufacturing. Complex geometries and internal structures that are difficult or impossible to achieve with conventional methods can be realized with 3D printing. There’s no need for additional complex tools or processes to create undercuts, overhangs, or intricate lattices. This freedom in design allows for the production of highly customized and elaborate objects, making it a powerful tool for handling complex designs.
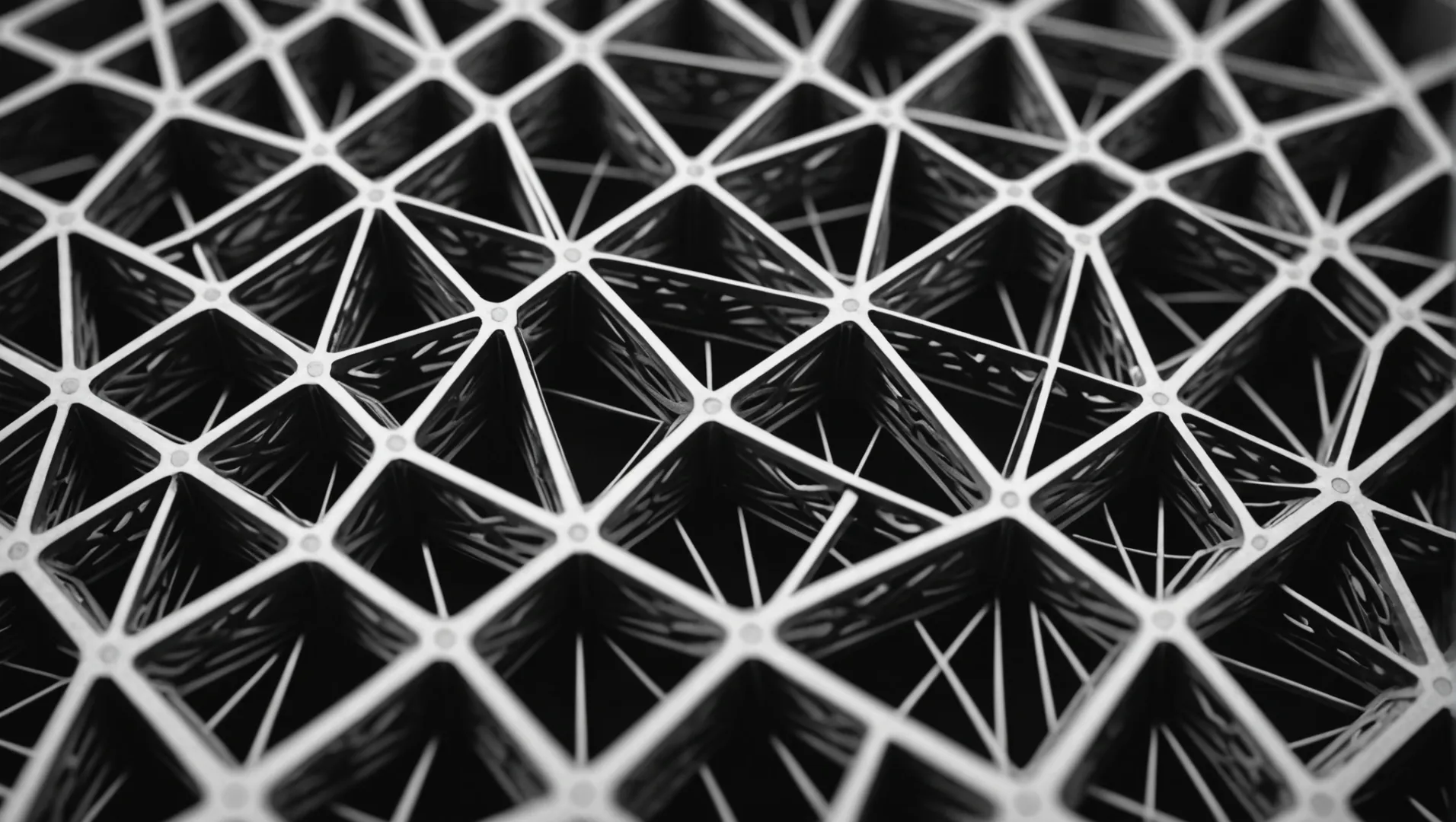
Understanding the Advantages of Layer-by-Layer Construction
3D printing’s unique additive manufacturing process builds objects layer by layer, allowing for unprecedented design freedom. Unlike traditional methods that may struggle with intricate geometries, 3D printing can efficiently produce complex designs with minimal limitations. This is particularly advantageous for industries like aerospace and biomedical engineering, where precision and customization6 are critical.
Overcoming Traditional Manufacturing Limitations
Traditional manufacturing techniques often face challenges with complex designs due to constraints in tooling and mold making. With 3D printing, these constraints are significantly reduced. For example, creating a heat exchanger with complex internal channels is labor-intensive with conventional methods. In contrast, a 3D printer can fabricate the entire structure seamlessly. This ability not only enhances the efficiency of prototyping but also improves the functional accuracy of the end product.
Designing for Complexity: Practical Applications
Designers can explore innovative concepts without being restricted by the physical limitations of traditional manufacturing. 3D printing supports complex lattice structures that offer high strength-to-weight ratios, which are invaluable in reducing weight in automotive and aerospace applications. Additionally, the capacity to produce bionic designs, inspired by natural forms, enables advancements in medical implants and prosthetics.
| Traditional Manufacturing | 3D Printing |
|---|---|
| Requires molds/tooling | No molds required |
| Limited by tool paths | Unlimited geometrical freedom |
| Material waste from cutting | Additive process minimizes waste |
The Role of Software in Managing Complexity
Software plays a pivotal role in the design process for 3D printing. With advanced CAD tools, designers can simulate and analyze complex structures before printing, ensuring functionality and structural integrity. The integration of AI and machine learning enhances this capability by optimizing designs for performance and manufacturability.
By leveraging these attributes, 3D printing not only meets but exceeds the demands of complex design projects, opening new avenues for innovation across various sectors.
3D printing requires molds for complex designs.False
3D printing eliminates the need for molds, allowing design freedom.
3D printing minimizes material waste in manufacturing.True
The additive process of 3D printing reduces material waste.
How Does In-House 3D Printing Improve Workflow Efficiency?
Bringing 3D printing capabilities in-house can revolutionize a company’s workflow, enhancing efficiency and innovation.
In-house 3D printing improves workflow efficiency in several ways. It shortens lead times as there’s no need to wait for external suppliers. Costs are reduced by eliminating outsourcing expenses. Rapid prototyping on-site enables immediate design iterations. This allows companies to quickly modify and improve their products. They can maintain better control over the production process, ensuring quality and timely completion. Moreover, it fosters a more collaborative environment among teams involved in design, engineering, and production, leading to enhanced overall efficiency.

Reducing Lead Times with On-Site Production
When companies integrate in-house 3D printing capabilities7, they significantly cut down the lead times associated with outsourcing prototyping and production. The immediate access to 3D printing equipment allows teams to quickly transform digital designs into physical prototypes without waiting for external suppliers.
For example, a product design team can take an idea from a digital model to a tangible prototype in just hours. This immediacy facilitates quick feedback loops and design iteration, which is crucial in fast-paced industries where time-to-market can define success or failure.
Cost-Effectiveness of In-House Solutions
While initial setup costs for 3D printing equipment can be high, the long-term savings are substantial. By eliminating the need for external vendors, companies save on both labor and shipping costs. Additionally, the reduction in material waste due to additive manufacturing processes further contributes to cost savings.
Consider a scenario where a company frequently requires small-batch prototypes. Traditionally, this would involve significant tooling costs for each batch. However, with 3D printing, each new design iteration can be produced at minimal additional cost, making the process much more economical.
Fostering Innovation and Collaboration
Having 3D printers on-site encourages a culture of innovation. Teams are more likely to experiment with new ideas when they can quickly produce and test prototypes without bureaucratic delays. This environment nurtures creativity and allows for more dynamic collaboration among team members.
In practical terms, designers and engineers can work closely with marketing teams to refine product aesthetics and functionality based on real-time feedback. A tangible model of a product concept enables more effective communication across departments, leading to better-aligned projects and innovative solutions.
Enhancing Control Over the Production Process
In-house 3D printing offers greater control over the entire production process. Teams can oversee every stage of prototyping and adjust parameters as needed to improve product quality. This control is particularly beneficial when dealing with sensitive designs or proprietary technology that require strict confidentiality.
Moreover, by keeping production in-house, companies can maintain better quality assurance standards and ensure that prototypes meet exact specifications before scaling up to mass production.
Versatility in Design and Material Choices
The flexibility of 3D printing technology allows teams to experiment with a wide range of materials and complex geometries that traditional methods might struggle with. Whether it’s lightweight lattice structures or intricate internal channels, the possibilities are virtually limitless.
For example, in the aerospace industry, where weight reduction is critical, companies can utilize in-house 3D printing to prototype components with complex internal structures that optimize weight without compromising strength.
In-house 3D printing reduces lead times significantly.True
On-site production eliminates delays from external suppliers, speeding up prototyping.
3D printing increases material waste in production.False
Additive manufacturing minimizes waste by using only necessary material for prototypes.
Conclusion
3D printing isn’t just about speed; it’s a gateway to innovation. By embracing this technology, you can enhance your design capabilities and bring ideas to life like never before.
-
Understand how design flexibility speeds up prototyping.: Increase design iteration and quantity by printing many different models at once. Make realism a priority through predictable colors, feel, and function. Help … ↩
-
Learn how avoiding tooling speeds up production.: 3D printing reduces tooling costs, increases flexibility, shortens lead times and improves quality. It is used in many manufacturing sectors today. ↩
-
Discover how single-unit production enhances speed.: Find out how 3D printing technology impact manufacturers with faster prototyping, on-demand production, and the ability to create complex! ↩
-
Explore how 3D printing eliminates tooling costs and enhances innovation.: Cost savings of up to 70% can be attributed to 3D printing due to prototyping. This is in contrast to traditional manufacturing, which is highly expensive. ↩
-
Discover how versatile materials in 3D printing reduce prototyping costs.: SLA 3D printing is highly versatile, offering resin formulations with a wide range of optical, mechanical, and thermal properties to match those of standard, … ↩
-
Explore how precision boosts innovation in complex design industries.: Customization: Every customer is unique, and 3D printing allows businesses to cater to specific customer needs without extensive retooling or setup changes. ↩
-
Discover why in-house 3D printing is a strategic advantage.: The main pros of a 3D printed home are the opportunities for new designs, reduced costs and fewer construction errors. All in all, this leads … ↩



