
When I first stumbled upon laser technology, I was amazed by its potential! But then I faced a dilemma: should I choose laser marking or laser engraving for my project? Let’s explore this together!
Laser marking differs from laser engraving in its approach and application. Marking alters the material surface without cutting into it, whereas engraving removes material to create a design. This difference affects speed, depth, and material suitability.
Understanding the nuances between laser marking and engraving can significantly impact your project’s outcome. Whether you’re considering industrial applications or artistic designs, knowing which technique best suits your needs is crucial. Dive deeper as we explore the specifics of each process.
Laser marking alters material without cutting into it.True
Laser marking changes the surface color or texture without material removal.
What Are the Key Features of Laser Marking Machines?
Laser marking machines are revolutionizing industries by providing precision, speed, and versatility in marking processes. But what makes them stand out?
Key features of laser marking machines include high precision, speed, versatility in material handling, and minimal maintenance needs. They utilize non-contact processes for marking, ensuring clean and durable results without altering the material’s integrity. Ideal for serial numbers, barcodes, and logos on various materials.

Precision and Accuracy
Laser marking machines are renowned for their precision. The laser beam can be focused to an extremely fine point, allowing for highly detailed markings that are critical for intricate designs or small fonts. This precision ensures that marks are clear and readable, which is essential for applications like barcoding or serial numbering.
Speed and Efficiency
With advancements in laser technology, these machines operate at remarkable speeds. The use of red-light laser heads enables faster operations compared to traditional methods. This speed does not come at the cost of quality, as the precision remains intact. This makes laser marking machines particularly effective in high-volume production environments where time is a critical factor.
Versatility in Material Handling
Laser markers can handle a wide array of materials, ranging from metals and plastics to glass and ceramics. This versatility is due to the non-contact nature of the process, which means that there is no physical wear or tear on the machine parts. The ability to mark on diverse materials without compromising the integrity of the surface is a significant advantage.
Table: Material Suitability for Laser Marking
| Material | Suitability | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Metals | High | Serial numbers, barcodes |
| Plastics | High | Branding logos, batch codes |
| Glass | Moderate | Decorative patterns, safety marks |
| Ceramics | Moderate | Industrial part labeling |
Minimal Maintenance
Laser marking machines require minimal maintenance compared to other traditional marking methods. The non-contact operation reduces wear and tear on machine components, thus extending the machine’s lifespan and reducing downtime. This aspect ensures consistent performance over time, making it a cost-effective solution for businesses.
Explore different laser technologies1 to understand their specific advantages and potential applications across various industries.
Laser marking ensures material integrity.True
Laser marking is non-contact, preserving material integrity.
Laser marking is slow and inefficient.False
Laser marking is fast and efficient, ideal for high-volume tasks.
How Do Laser Engraving Machines Operate?
Laser engraving machines revolutionize the way we etch designs, providing precision and versatility for various materials.
Laser engraving machines operate using a focused laser beam to remove material, creating precise and permanent designs. They utilize a mechanical system that moves the laser head along X and Y axes, allowing for detailed engraving across a larger surface area.
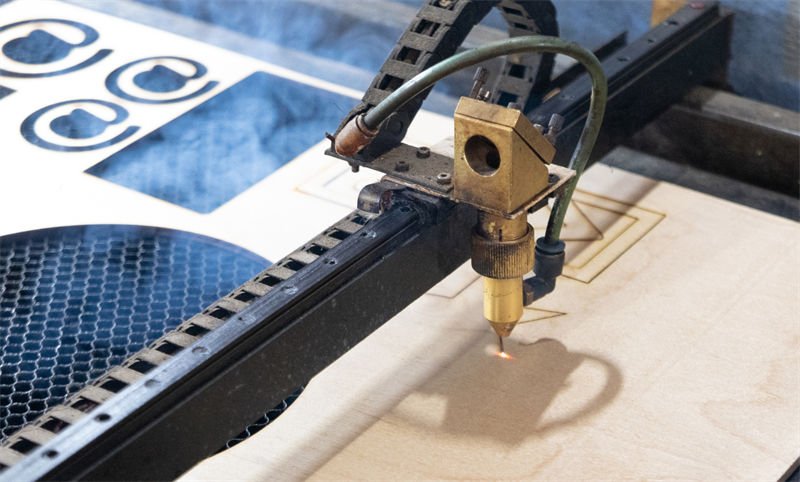
Understanding the Mechanics of Laser Engraving
Laser engraving machines are sophisticated devices that employ high-powered laser beams to cut into material surfaces. Unlike laser marking, which simply alters the surface color, engraving physically removes material to create depth and texture. This process is achieved through a combination of laser technology2 and mechanical movement.
The Role of X and Y Axes
A key feature of laser engraving machines is their reliance on a mechanical drive system. This system operates on X and Y axes, enabling the laser head to traverse a wide surface area without losing focus. This movement allows for intricate designs and patterns to be engraved with high precision.
Here’s a breakdown of how the axes work:
| Axis | Functionality |
|---|---|
| X | Moves the laser horizontally across the material |
| Y | Moves the laser vertically, complementing X-axis motion |
Focusing the Laser Beam
The focus of the laser beam is crucial for effective engraving. These machines typically use blue-light laser heads, which are adept at focusing the beam precisely to achieve the desired depth in materials like wood, leather, and acrylic. Laser head3 adjustment ensures that the beam maintains its intensity and precision as it moves over varying surface contours.
Applications and Material Compatibility
Laser engraving is highly versatile and suitable for numerous applications. It can be used to:
- Create intricate patterns on jewelry and decorative items
- Engrave text and logos on metal tools
- Cut complex shapes out of acrylic sheets for signage
The choice of material significantly impacts the engraving process. While materials like wood and leather are ideal due to their ability to absorb energy effectively, metals may require higher-powered lasers.
Benefits Over Other Methods
Compared to traditional engraving methods, laser engraving offers several advantages:
- Speed and Precision: The automated movement ensures quick processing with minimal error.
- Versatility: Capable of working on diverse materials, from delicate glass to sturdy metals.
- Cost-Efficiency: Reduced need for manual labor and tool maintenance.
By understanding these operational aspects, you can better appreciate how laser engraving machines transform simple materials into intricate works of art.
Laser engraving machines use a laser beam to mark surfaces.False
They engrave by removing material, not just marking surfaces.
Laser engraving requires movement along X and Y axes.True
The laser head moves horizontally and vertically for detailed designs.
Which Materials Are Best Suited for Each Process?
Choosing the right material for laser processes can enhance efficiency and quality. Discover which materials excel in marking versus engraving.
Materials suited for laser marking include metals and plastics, where surface alterations are needed without depth. For laser engraving, wood and acrylic are ideal due to their ability to handle deeper cuts and textural changes.

Understanding Material Suitability
In the realm of laser processing, selecting the appropriate material is as crucial as choosing the right machine. The efficiency, precision, and quality of the end result heavily depend on this choice. Both laser marking and laser engraving have unique requirements and outcomes that necessitate different materials.
Laser Marking Materials
Laser marking is primarily used for creating precise, durable marks on material surfaces without altering their structure. Thus, it is essential to choose materials that respond well to surface modifications:
- Metals: Stainless steel, aluminum, and titanium are commonly used because they can handle fine and permanent marks without material degradation.
- Plastics: Polycarbonate and ABS plastic are popular due to their ability to produce clear markings with minimal surface damage.
- Glass: Ideal for marking intricate designs or information without compromising the glass’s integrity.
The table below summarizes materials suitable for laser marking:
| Material | Features |
|---|---|
| Metals | Durable, precise marks |
| Plastics | Minimal surface damage |
| Glass | Intricate design compatibility |
Laser Engraving Materials
Engraving involves removing material to create deeper designs, necessitating substrates that can withstand cutting and shaping:
- Wood: Softwoods like pine are easy to engrave due to their texture and adaptability.
- Acrylic: Known for its smooth surface that allows for clean, deep engravings.
- Leather: Provides a unique texture and aesthetic when engraved, often used in custom goods.
The table below highlights materials best suited for laser engraving:
| Material | Features |
|---|---|
| Wood | Easy engraving, adaptable texture |
| Acrylic | Smooth surface, clean engravings |
| Leather | Unique texture, aesthetically pleasing |
Factors Influencing Material Choice
Selecting the right material involves understanding the specific needs of your project. Consider these factors:
- Project Requirements: Determine whether speed or depth is your priority. Laser marking is faster but doesn’t offer depth, making it perfect for high-speed industrial tasks.
- Material Properties: Evaluate the heat tolerance and physical properties of the material. Some materials may discolor or warp under heat.
- End-use Application: Consider the environment where the marked or engraved item will be used. For instance, markings on metals used in outdoor settings need to be resistant to wear and corrosion.
By understanding these elements, you can make an informed decision about which laser process and materials will yield the best results for your specific applications.
Metals are ideal for laser marking.True
Metals like stainless steel handle fine, permanent marks well.
Wood is unsuitable for laser engraving.False
Wood is ideal for engraving due to its texture and adaptability.
When Should You Choose Laser Marking Over Engraving?
Choosing between laser marking and engraving can define the success of your project. But when is marking the better option?
Choose laser marking over engraving when speed, precision, and surface integrity are priorities. It’s ideal for creating permanent, non-invasive markings on sensitive materials like metals and plastics, without affecting their structure.

Understanding the Functional Difference
The fundamental decision to choose laser marking over engraving hinges on understanding their functional differences. Laser marking is a process where a laser beam interacts with the surface of a material, causing a change in its appearance through oxidation, chemical alteration, or ablation. This method is particularly effective when you need to mark surfaces without cutting into the material itself.
Conversely, laser engraving4 involves removing layers of material to achieve depth and texture, making it suitable for artistic designs or where tactile features are desired. The key is to decide whether surface modification or material removal better suits your needs.
Application and Material Suitability
Laser marking is frequently chosen over engraving for industrial applications where quick, precise marks such as barcodes, serial numbers, and logos are needed. These markings are crucial for product identification and traceability. The process works exceptionally well on metals, ceramics, and plastics because it maintains the structural integrity of these materials.
For instance, in the automotive industry, laser marking is preferred for components that require clear identification but must remain structurally sound. Similarly, in electronics, circuit boards often use laser marking due to its non-invasive nature.
Speed and Efficiency Considerations
If your project demands rapid processing times, laser marking has the upper hand. It operates at higher speeds compared to engraving, making it ideal for batch productions where time efficiency is critical. This is particularly advantageous in settings like assembly lines, where throughput can be dramatically improved.
Table: Comparison of Laser Marking and Engraving
| Feature | Laser Marking | Laser Engraving |
|---|---|---|
| Depth | Surface-level | Deep penetration |
| Speed | Faster | Slower |
| Material Impact | Minimal | Significant |
| Best For | Serial numbers, logos | Artistic designs, deep textures |
Long-term Durability and Aesthetics
In situations where durability and aesthetic appeal are critical, laser marking excels. The process ensures that the markings remain clear and legible throughout the product’s lifecycle, enduring wear and tear without degradation. This durability is essential in sectors like aerospace and medical devices, where permanent identification is mandatory.
Moreover, the aesthetic aspect of laser marking is noteworthy. The technique can produce high-contrast marks that are visually appealing without altering the material’s surface texture. This makes it an excellent choice for luxury goods where maintaining the material’s pristine condition is paramount.
In conclusion, choosing between laser marking and engraving should be informed by your project’s specific needs. Consider factors like material type, desired speed, and the importance of maintaining material integrity when making your decision.
Laser marking is faster than engraving.True
Laser marking operates at higher speeds, ideal for rapid processing.
Engraving maintains material integrity better than marking.False
Laser marking preserves structural integrity, unlike engraving.
Conclusion
Choosing between laser marking and engraving depends on your project’s demands. Marking is ideal for speed and surface precision, while engraving offers depth and texture. Evaluate your needs to make an informed decision.
-
Understand various laser technologies to choose the best for your needs.: What Is a Laser? · Gas Lasers · Solid-State Lasers · Fiber Lasers · Liquid Lasers (Dye Lasers) · Semiconductor Lasers (Laser Diodes) · Laser Types by … ↩
-
Learn about the fundamentals of laser technology in engraving.: Laser engraving technically explained. During the process of laser engraving, the laser beam impinges on the material, exposing it to a great deal of heat. ↩
-
Discover why blue-light heads are preferred in detailed engravings.: Blue light laser engraving machines use shorter wavelength blue light as the engraving light source, with higher resolution and smaller spot diameter. This … ↩
-
Explore detailed differences between engraving and marking techniques.: Laser marking discolors the surface of the material, while laser etching and engraving actually removes a portion of the surface area as it … ↩



